Overview
The body parts that are prone to fungal infections include the skin, hair, and nails. The most fundamental step in determining the fungus that causes an infection is to establish what causes the itch. Having the appropriate knowledge about how to determine an infection can help in preventing the infection from recurring. It can also help in preventing the development of serious infections in the body.
Athlete’s Foot
This is one of the common fungal infections. People suffering from this condition have red and puffy skin around their feet. Other classic symptoms of the condition include moisture in the area between your toes and around your soles. Itching and burning are also common symptoms in people with athlete’s foot. Ordinary retail medications can cure athlete’s foot. If these medications fail to produce positive results after one week of use, it is vital to visit your podiatrist for assistance.
Jock Itch
This is also one of the common fungal infections. It mainly occurs on the armpits, the groin, and beneath the breasts. Jock itch results from moisture that accumulates after engaging in strenuous physical activities or during hot days.
Cornstarch powder is an effective remedy for persons with excessive creases or folds on their body. This treatment prevents the infection from occurring and keeps you dry and cool.
Ringworm
This fungal infection is common in children. It is acquired via body-to-body contact with infected people or animals. The key symptom of this condition is a radial patch on the infected area of your skin. It usually begins as a red bump, which develops into a red circular patch. The patch continues to grow in size with time. Traditional retail antifungal creams can treat ringworm. Apply antifungal creams for 2 extra weeks even after the patch has healed. Consider using oral antifungal medicines if you have an extensive infection like a scalp infection.
Check the Nails
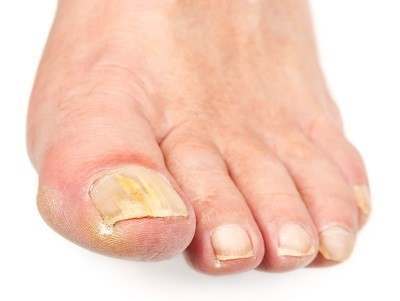 Fungal nail infections mainly occur in adults compared to children. A person with this infection has thickened nails at the sides and the fingertips. Eventually, the bed of the nail becomes infected, causing the entire nail to thicken. The nail then becomes yellow or creamy and opaque. At last, small patches and streaks occur and the nail darkens over time. Persons suffering from peripheral artery disease or diabetes and have persistent skin or nail fungal infections are at a higher risk of acquiring secondary skin infections that are caused by bacteria.
Fungal nail infections mainly occur in adults compared to children. A person with this infection has thickened nails at the sides and the fingertips. Eventually, the bed of the nail becomes infected, causing the entire nail to thicken. The nail then becomes yellow or creamy and opaque. At last, small patches and streaks occur and the nail darkens over time. Persons suffering from peripheral artery disease or diabetes and have persistent skin or nail fungal infections are at a higher risk of acquiring secondary skin infections that are caused by bacteria.
Oral medications provide the best remedy for fungal nail infections. The most common oral prescription involves at least three months of treatment for toenail infections and up to six weeks for fingernail infections.
Contacting a Physician
The best method to ascertain whether a fungus has infected you is to contact your physician for help. Numerous skin conditions may resemble fungal infections. Therefore, it is important to know the best possible medications for your condition. In case you develop a skin rash, your physician may take a small sample by scraping the irritated area of the skin. The physician then observes the sample under a microscope to determine whether a fungus is the cause of your skin problem.